Both boiling water and using a reverse osmosis drinking water system are effective ways of making water pure and healthier to drink, but they are not the same and neither one is guaranteed to produce 100% pure water. Is boiled water better than RO water?
Boiling water will kill organic organisms and unwanted pathogens and VOCs in water. A reverse osmosis filtering system will remove dissolved solids and can also remove organics, microbes, metals, and more from water.
Here’s What We Will Be Covering!
- What Does Boiling Water Remove?
- What Does Reverse Osmosis Remove From Water?
- 20 Common Impurities That Can Be Removed Using Reverse Osmosis.
- How Does Reverse Osmosis Remove Contaminants That Boiling Can’t?
What Does Boiling Water Remove?
When you boil water, the heat that is created is capable of destroying organic material such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, and some Volatile Organic Compounds (commonly known as VOCs) contained in water.
In order to accomplish this, the water must be boiled for a minimum of 20 minutes to kill all of the organic contaminants in the water. Since the number of contaminants in the water is usually unknown, it is very hard to be sure that water will be free of organic contaminants after boiling. (source)
Although boiling water for a long enough amount of time will kill all of the potentially harmful organic materials in the water, this does not mean that the water will stay healthy to consume for a long period of time.
Any water that is exposed to air can quickly become a breeding ground for bacteria or harmful pathogens. Water that has been purified by boiling should be consumed soon after to be sure that it is still pure enough to be considered healthy.
When water is boiled, the dissolved solids contained in the water will not be removed by the heat created, but a portion of the water will be dissipated as steam.

This means that the concentration of the dissolved solids in the water will increase, meaning that the number of dissolved solids consumed per ounce of water will be higher than in the original water sample.
Although the dissolved solids contained in water can be many things, the primary dissolved solid in residential water is salt. Salt is not considered to be harmful to humans but an excessive amount of salt can cause dehydration, high blood pressure, and other health problems.
Because of this, a reverse osmosis system is highly recommended because it removes a very high percentage of dissolved solids contained in water.
What Does Reverse Osmosis Remove From Water?
Because reverse osmosis is a process of filtering out fine particles and dissolved solids from water, it can remove contaminants from water that boiling will not.
A reverse osmosis system will remove most if not all of many chemicals including salts, metals like copper and lead, harmful contaminants like arsenic, radium, and pesticides, and even minerals in water that contribute to water being hard like magnesium and calcium.
20 Common Impurities That Can Be Removed Using Reverse Osmosis.
| Impurity | Rejection(Removal) % |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 85 – 94% |
| Sulfate | 96 – 98% |
| Calcium | 94 – 98% |
| Potassium | 85 – 95% |
| Nitrate | 60 – 75% |
| Iron | 94 – 98% |
| Zinc | 95 – 98% |
| Mercury | 95 – 98% |
| Selenium | 94 – 96% |
| Lead | 95 – 98% |
| Phosphate | 96 – 98% |
| Arsenic | 92 – 96% |
| Magnesium | 94 – 98% |
| Nickel | 96 – 98% |
| Fluoride | 85 – 92% |
| Manganese | 94 – 98% |
| Cadmium | 95 – 98% |
| Barium | 95 – 98% |
| Cyanide | 84 – 92% |
| Chloride | 85 – 92% |
How does reverse osmosis remove contaminants that boiling can’t?
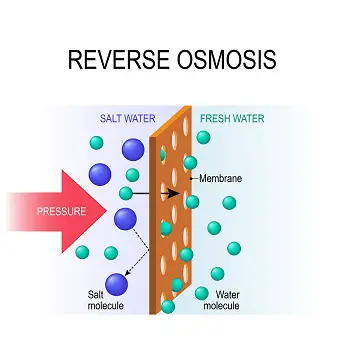
The basic reverse osmosis drinking water system consists of a fine particle pre-filter, a semi-permeable membrane, and a carbon post (last) filter.
The fine particle pre-filter will filter out fine sediment and other fine particles that are suspended in the water entering the reverse osmosis system.
This filter is not only filtering out the particles to make the water better for you to consume, but it is also protecting the rest of the reverse osmosis system from these particles that can damage the membrane of the system.
The reverse osmosis membrane is the heart of the reverse osmosis drinking water system. This membrane is semi-permeable. This means that it will allow water to go back and forth through it but will reject unwanted particles and discharge them to waste.
This process of particle rejection is why a semi-permeable membrane is different than a regular filter.
If a drinking water system used a super-fine filter to remove dissolved solids from water that did not allow water to flow both ways through it, the filter would get a build-up of dissolved solids very quickly and the filter would have to be changed very often.
A reverse osmosis membrane gets cleaned off during the reverse osmosis process so it can potentially last for many years and continue to filter out dissolved solids with minimal loss of effectiveness.
The last filtering process in most reverse osmosis drinking water systems is a carbon-based filter that can remove fine particles that can give water a bad taste or cause it to have unpleasant odors. This final polishing filter leaves the water considerably purer and more enjoyable to drink or cook with.
To Sum Up:
Water that has potentially harmful organic organisms contained in it can be boiled to kill the organics in it and make it safer to consume, although this does not necessarily make the water healthy.
Using a reverse osmosis drinking water system will greatly remove unhealthy dissolved solids in water and many reverse osmosis systems can also remove harmful organic organisms contained in water using filtering and ultraviolet light.
Boiling questionable water is a great first step to creating safe water, but using a reverse osmosis drinking water system will provide water that is more pure than boiling and is more reliable than boiling.
If you are going to do any work on your reverse osmosis drinking water system, check out my article What I Use When I Work On A Reverse Osmosis System!

